SPLIT AIR CONDITIONERS
HOW IT WORKS
1. Furnace - component that circuates air and adds heat to the air by burning gas.
2. Coil - transfers interior heat into the refrigerant lines and moves that heat outdoors.
3. Condenser - removes heat from the house.
4. Supply Air - Sends into rooms after being heated or cooled.
5. Refrigerant Lines - medium by which heat is transfered from one place to another.
6 Return Air- returns air into the heating and cooling system.
7. Humidifier - device that increase humidity.
8. Air Cleaner - removes solid particulate matter such as dust, polen, mold, and bacteria from the air depending on the type of filter and efficiency level.

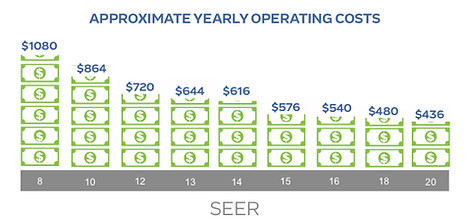

COOL YOUR HOME FOR LESS
Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is the rate by which all air conditioning and heat pump energy efficiently is measured. In the world of cooling, the higher the SEER, the better the efficiency and the lower your energy bills.
HEAT YOUR HOME FOR LESS
Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) measures the amount of heat actually delivered to your house compared to the amount of fuel supplied to the furnace. For example, a furnace that has an 80% AFUE rating converts 80% of the fuel to heat - the other 20% is vented out to your roof as wasted money. The higher the AFUE rating, the better the energy efficiency and the less money you waste.
Most systems 15 years or older are rated around 65% AFUE. Upgrading to a Einstein modulating furnace rated at 97% AFUE can save around $1,694 a year on energy costs. And of course, as the cost of natural gas rises, you'll save even more.
.png)
